The Indian Armed Forces stand as one of the world’s largest and most formidable military organizations, dedicated to safeguarding India’s sovereignty and interests. Comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force, the Indian Armed Forces operate under a well-defined military structure that emphasizes discipline, hierarchy, and specialized roles. In this guide, we’ll break down the structured ranks and roles within each branch, helping you understand how they function and contribute to national defense. Whether you’re a military enthusiast, a student, or someone exploring career options in the Indian Armed Forces, this overview will provide valuable insights.
Overview of the Indian Armed Forces Structure
The Indian Armed Forces are divided into three primary branches: the Indian Army, Indian Navy, and Indian Air Force. Each branch has its own rank hierarchy, but they share common principles of command and control. Ranks in the Indian Armed Forces are categorized into officers and other ranks (enlisted personnel). Officers hold leadership positions, while other ranks perform operational duties.
The military structure is designed for efficiency, with ranks denoting authority, responsibilities, and pay scales. Promotions are based on merit, experience, and performance. Key elements include:
Commissioned Officers: Trained leaders who command units.
Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs): Bridge between officers and enlisted personnel.
Other Ranks: Enlisted soldiers, sailors, or airmen handling frontline tasks.
This structured approach ensures seamless coordination during operations, from peacekeeping missions to border security.
Indian Army Ranks and Roles
The Indian Army, the largest branch, focuses on land-based warfare, including infantry, artillery, and armored divisions. Its ranks reflect a pyramid structure, with generals at the top and sepoys at the base.
Officer Ranks and Roles
Field Marshal: The highest rank, rarely awarded (e.g., to Sam Manekshaw). Role: Supreme commander in wartime.
General: Chief of Army Staff (COAS). Role: Oversees army operations and strategy.
Lieutenant General: Commands corps or key formations. Role: Regional leadership and planning.
Major General: Leads divisions. Role: Tactical command and administration.
Brigadier: Commands brigades. Role: Field operations and unit management.
Colonel: Senior staff officer. Role: Advisory and specialized roles like intelligence.
Lieutenant Colonel: Battalion commander. Role: Direct troop leadership.
Major: Company commander. Role: Training and combat leadership.
Captain: Platoon leader. Role: Frontline command and coordination.
Lieutenant: Junior officer. Role: Assistant roles in units.
Other Ranks and Roles
Subedar Major: Senior JCO. Role: Regimental administration.
Subedar: Company JCO. Role: Unit discipline and training.
Naib Subedar: Platoon JCO. Role: Tactical support.
Havildar: Section leader. Role: Squad command and logistics.
Naik: Assistant section leader. Role: Support in combat.
Lance Naik: Junior enlisted. Role: Specialized tasks like driving or signals.
Sepoy: Basic soldier. Role: Infantry duties, security, and patrols.
The Indian Army’s roles emphasize versatility, from counter-insurgency in Kashmir to disaster relief, showcasing its structured ranks in action.
Indian Navy Ranks and Roles
The Indian Navy protects maritime interests, including coastal defense and naval warfare. Its ranks blend naval traditions with modern naval technology, focusing on ships, submarines, and aviation.
Officer Ranks and Roles
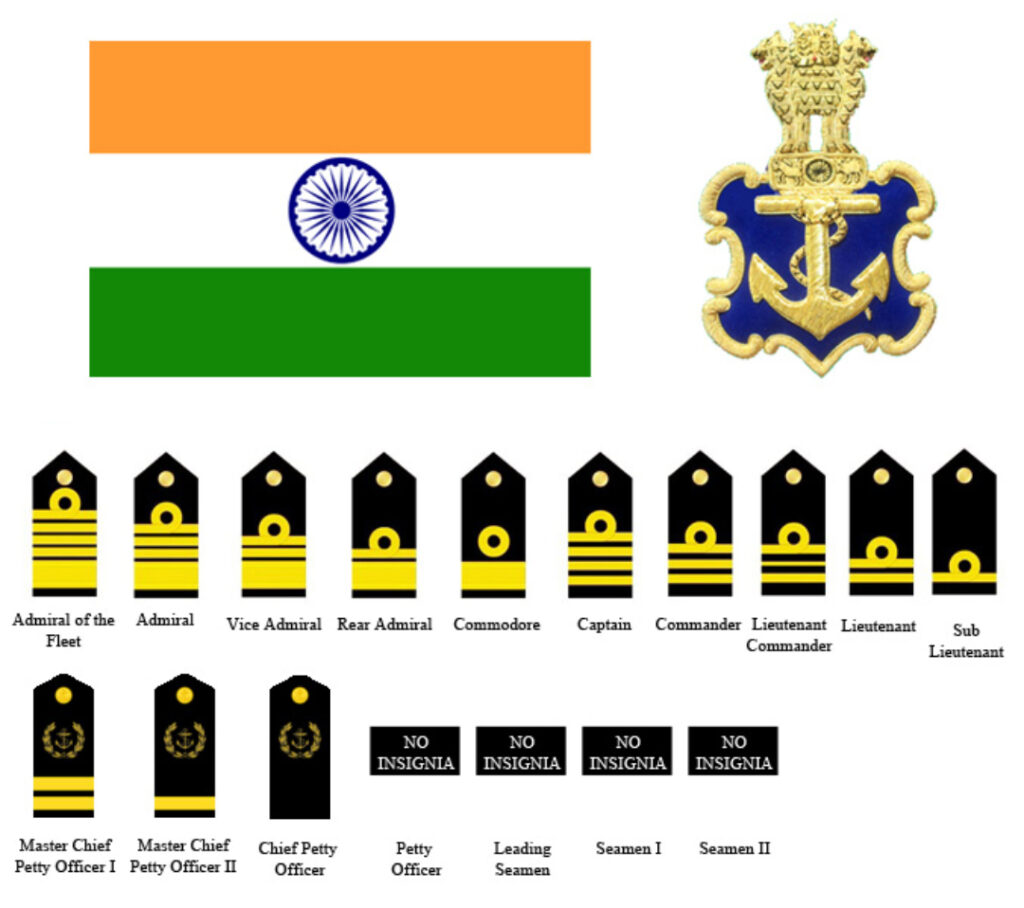
Admiral: Chief of Naval Staff (CNS). Role: Overall naval command and strategy.
Vice Admiral: Commands fleets or naval commands. Role: Operational leadership.
Rear Admiral: Leads squadrons or bases. Role: Tactical and administrative oversight.
Commodore: Senior officer in charge of smaller units. Role: Specialized commands like submarines.
Captain: Ship commander. Role: Vessel operations and crew management.
Commander: Executive officer on ships. Role: Coordination and planning.
Lieutenant Commander: Department head. Role: Technical and combat roles.
Lieutenant: Junior officer. Role: Watchkeeping and training.
Sub-Lieutenant: Entry-level officer. Role: Initial command duties.
Other Ranks and Roles
Master Chief Petty Officer: Senior enlisted. Role: Fleet administration.
Chief Petty Officer: Section leader. Role: Technical expertise on ships.
Petty Officer: Team supervisor. Role: Maintenance and operations.
Leading Seaman: Skilled sailor. Role: Specialized tasks like gunnery.
Able Seaman: Basic sailor. Role: Deck duties and navigation.
The Indian Navy’s structured ranks support roles in anti-piracy operations, like in the Gulf of Aden, and carrier-based aviation, highlighting its global reach.
Indian Air Force Ranks and Roles
The Indian Air Force (IAF) handles aerial defense, including fighter jets, bombers, and transport aircraft. Its ranks prioritize air superiority and rapid response.

Officer Ranks and Roles
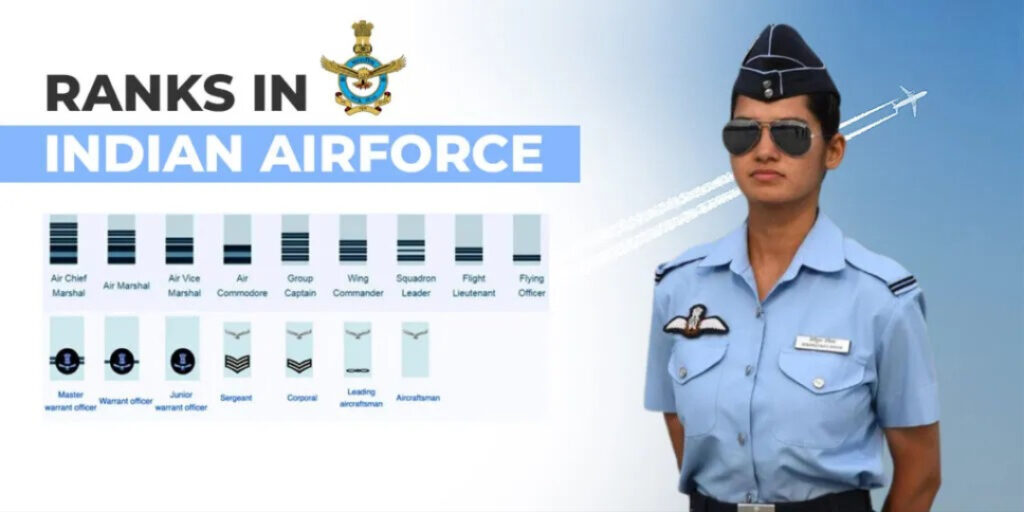
Air Chief Marshal: Chief of Air Staff (CAS). Role: Aerial strategy and force management.
Air Marshal: Commands air commands. Role: Regional air operations.
Air Vice Marshal: Leads airbases or wings. Role: Tactical planning.
Air Commodore: Senior wing commander. Role: Unit leadership.
Group Captain: Squadron leader. Role: Flight operations and training.
Wing Commander: Flight commander. Role: Direct aerial command.
Squadron Leader: Section leader. Role: Pilot and mission coordination.
Flight Lieutenant: Junior pilot. Role: Combat and support roles.
Flying Officer: Entry-level officer. Role: Initial flying duties.
Other Ranks and Roles
Master Warrant Officer: Senior enlisted. Role: Ground crew administration.
Warrant Officer: Technical supervisor. Role: Aircraft maintenance.
Sergeant: Team leader. Role: Logistics and support.
Corporal: Assistant leader. Role: Ground operations.
Leading Aircraftman: Skilled airman. Role: Specialized tasks like radar.
Aircraftman: Basic airman. Role: Base duties and security.
The IAF’s structured ranks enable roles in air defense, such as during the 2019 Balakot strikes, demonstrating precision and technology integration.
How Understanding Ranks Helps in Defence Exam Preparation
Aspiring officers must grasp the Indian Armed Forces’ structured ranks and roles to excel in competitive exams like CDS, AFCAT, NDA, and SSB interviews. Knowing these hierarchies not only aids in written tests but also prepares you for SSB discussions, where leadership and military knowledge are key. At The Lakshya Academy, we specialize in CDS, AFCAT, NDA, and SSB preparation, offering tailored courses that cover exam strategies, physical training, and insights into military life. Our expert faculty ensures you understand not just the ranks but how they apply in real-world scenarios, boosting your chances of success. Enroll today to turn your defence dreams into reality!
Conclusion: The Backbone of India's Defense
Understanding the structured ranks and roles in the Indian Armed Forces reveals a system built on hierarchy, expertise, and unity. From the Army’s ground prowess to the Navy’s maritime dominance and the Air Force’s aerial supremacy, each branch’s ranks ensure effective defense. If you’re inspired to join, explore recruitment through the official Indian Armed Forces website or get expert guidance at The Lakshya Academy for CDS, AFCAT, NDA, and SSB prepration. Share your thoughts in the comments—do you have a favorite branch?